架设etcd集群
静态启动etcd集群需要每个成员在集群中知道另一个成员。在许多情况下,集群成员的IP可能提前未知。在这种情况下,可以使用etcd集群的自动发现服务。一旦etcd集群启动并运行,可以通过运行时重新配置完成添加或删除成员。
下面是三种典型的启动配置 具体参照官方介绍 etcd clustering
· 静态配置
· etcd发现
· DNS发现
下面将在以下三台主机上搭建etcd集群:
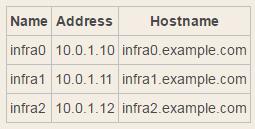
静态配置
因为我们知道集群成员,它们的地址和集群在启动之前的大小,我们可以使用离线引导配置,通过设置初始集群标志。每台机器将获得以下环境变量或命令行:
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER="infra0=http://10.0.1.10:2380,infra1=http://10.0.1.11:2380,infra2=http://10.0.1.12:2380"
ETCD_INITIAL_CLUSTER_STATE=new
--initial-cluster infra0=http://10.0.1.10:2380,infra1=http://10.0.1.11:2380,infra2=http://10.0.1.12:2380
--initial-cluster-state new
在每台机器上,使用以下标志启动etcd:
$ etcd --name infra0 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://10.0.1.10:2380
--listen-peer-urls http://10.0.1.10:2380
--listen-client-urls http://10.0.1.10:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
--advertise-client-urls http://10.0.1.10:2379
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1
--initial-cluster infra0=http://10.0.1.10:2380,infra1=http://10.0.1.11:2380,infra2=http://10.0.1.12:2380
--initial-cluster-state new
$ etcd --name infra1 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://10.0.1.11:2380
--listen-peer-urls http://10.0.1.11:2380
--listen-client-urls http://10.0.1.11:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
--advertise-client-urls http://10.0.1.11:2379
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1
--initial-cluster infra0=http://10.0.1.10:2380,infra1=http://10.0.1.11:2380,infra2=http://10.0.1.12:2380
--initial-cluster-state new
$ etcd --name infra2 --initial-advertise-peer-urls http://10.0.1.12:2380
--listen-peer-urls http://10.0.1.12:2380
--listen-client-urls http://10.0.1.12:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379
--advertise-client-urls http://10.0.1.12:2379
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-1
--initial-cluster infra0=http://10.0.1.10:2380,infra1=http://10.0.1.11:2380,infra2=http://10.0.1.12:2380
--initial-cluster-state new
以--initial-cluster开头的命令行参数在etcd的后续运行时将被忽略。在初始引导过程之后,可以随意删除环境变量或命令行标志。
CONFD
直接在Github上下载解压到对应目录就实现了安装
下面主要是confd搭配etcd进行nginx的自动配置
添加一些键值对
etcdctl set /myapp/database/url db.example.com
etcdctl set /myapp/database/user rob
创建配置文件目录
这个配置文件目录是用来存放配置文件和模板文件
sudo mkdir -p /etc/confd/{conf.d,templates}
创建资源配置文件
模板资源配置文件使用TOML配置文件格式来定义定义。
/etc/confd/conf.d/myconfig.toml
[template]
src = "myconfig.conf.tmpl"
dest = "/tmp/myconfig.conf"
keys = [
"/myapp/database/url",
"/myapp/database/user",
]
创建资源模板文件
资源模板文件采用Golang text templates格式定义
/etc/confd/templates/myconfig.conf.tmpl
[myconfig]
database_url = {{getv "/myapp/database/url"}}
database_user = {{getv "/myapp/database/user"}}
生成模板
confd支持守护程序和一次性操作两种操作模式。在守护程序模式下,confd轮询后端以进行更改,并在必要时更新目标配置文件。
confd -onetime -backend etcd -node http://127.0.0.1:4001
Note: The metadata api prefix can be defined on the cli, or as part of your keys in the template toml file.
输出:
2014-07-08T20:38:36-07:00 confd[16252]: INFO Target config /tmp/myconfig.conf out of sync
2014-07-08T20:38:36-07:00 confd[16252]: INFO Target config /tmp/myconfig.conf has been updated
目标配置文件已经生成
cat /tmp/myconfig.conf
输出:
# This a comment
[myconfig]
database_url = db.example.com
database_user = rob
配置使用使用生成nginx配置文件
这个例子将使用一个confd模板生成两个nginx配置文件
添加键值对
etcdctl set /myapp/subdomain myapp
etcdctl set /myapp/upstream/app2 "10.0.1.100:80"
etcdctl set /myapp/upstream/app1 "10.0.1.101:80"
etcdctl set /yourapp/subdomain yourapp
etcdctl set /yourapp/upstream/app2 "10.0.1.102:80"
etcdctl set /yourapp/upstream/app1 "10.0.1.103:80"
创建资源模板
/etc/confd/conf.d/myapp-nginx.toml
[template]
prefix = "/myapp"
src = "nginx.tmpl"
dest = "/tmp/myapp.conf"
owner = "nginx"
mode = "0644"
keys = [
"/subdomain",
"/upstream",
]
check_cmd = "/usr/sbin/nginx -t -c {{.src}}"
reload_cmd = "/usr/sbin/service nginx reload"
/etc/confd/conf.d/yourapp-nginx.toml
[template]
prefix = "/yourapp"
src = "nginx.tmpl"
dest = "/tmp/yourapp.conf"
owner = "nginx"
mode = "0644"
keys = [
"/subdomain",
"/upstream",
]
check_cmd = "/usr/sbin/nginx -t -c {{.src}}"
reload_cmd = "/usr/sbin/service nginx reload"
创建模板
/etc/confd/templates/nginx.tmpl
upstream {{getv "/subdomain"}} {
{{range getvs "/upstream/*"}}
server {{.}};
{{end}}
}
server {
server_name {{getv "/subdomain"}}.example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://{{getv "/subdomain"}};
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}

